Paediatric cardiology
Paediatric cardiologists diagnose and treat children with heart conditions before they are born, through childhood and into adulthood.
Your patients will be infants and children with complex diagnostic and medical problems, and you’ll work closely with specialist colleagues in a multidisciplinary team.
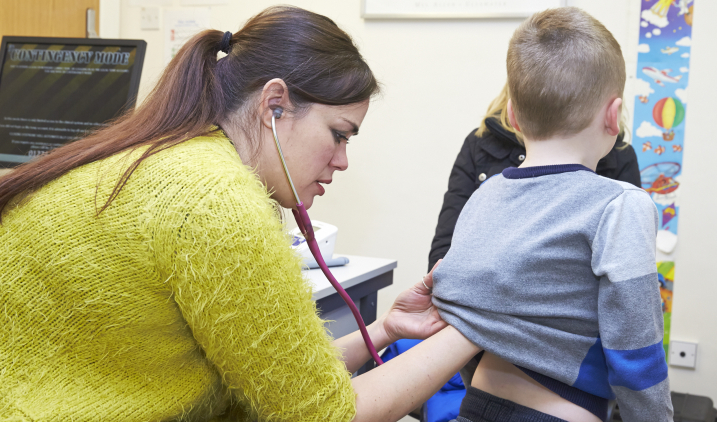
Life as a doctor in paediatric cardiology
You’ll use a range of advanced scanning and diagnostic techniques to assess conditions such as foetal cardiac abnormalities in the womb, heart failure in children and heart murmurs [1]. You’ll diagnose and treat conditions such as congenital heart disease that is present at birth, variations in heartbeat rhythms (arrhythmias) and problems with circulatory function. In some cases, a heart transplant may be required.
How much can I earn?
How about the benefits?
- make a difference
- flexible and part-time working
- high income early in your career
- work anywhere in the world
- excellent pension scheme
- good holiday entitlement
- NHS discounts in shops and restaurants
Must-have skills
- excellent communication skills to manage a wide range of relationships with colleagues, and patients and their families
- emotional resilience, a calm temperament and the ability to work well under pressure
- teamwork and the capacity to lead multidisciplinary teams
- problem-solving and diagnostic skills
- outstanding organisational ability and effective decision-making skills
- first-class time and resource management for the benefit of patients
Entry requirements
If you already have a degree, you could study for a four-year postgraduate degree in medicine.
What are my chances of starting a career in paediatric cardiology?
How to become a doctor in paediatric cardiology
After your foundation programme, you can apply for paid specialty training [6] to become a doctor in paediatric cardiology, which will take a minimum of eight years.
Where a career as a paediatric cardiologist can take you
- specialise or conduct research in areas such as foetal cardiology and adult congenital heart disease
- teach medical students or postgraduate students in training
Other roles that may interest you
- Cardiologist [56]
- General practitioner [57]
- Paediatrician [58]
- Paediatric surgery [59]
